Biofuels
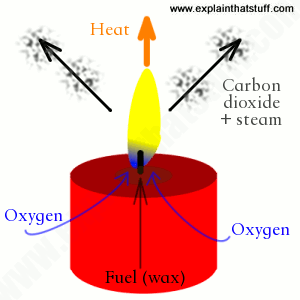
Coal and crude oil are non-renewable resources. They take so long to form that they cannot be replaced once they have all been used up. This means that these fossil fuels are likely to become more expensive as they begin to run out. Petrol, diesel and other fuels produced from crude oil make a range of harmful substances when they are burned, including:
- carbon dioxide
- carbon monoxide
- water vapour
- particulates (solid particles)
- sulfur dioxide
- oxides of nitrogen or NOx.
Biofuels are fuels produced from plant material. They have some advantages and disadvantages compared to fossil fuels.
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is made from rapeseed oil and other plant oils. It can be used in diesel-powered vehicles without needing any modifications to the engine.
Bioethanol
Ethanol, C2H5OH, is not a hydrocarbon because it contains oxygen as well as hydrogen and carbon. However, it is a liquid fuel that burns well. Bioethanol is made by fermenting sugars from sugar cane, wheat and other plants. It cannot be used on its own unless the engine is modified. However, modern petrol engines can use petrol containing up to 10 percent ethanol without needing any modifications, and most petrol sold in the UK contains ethanol.
Ethical concerns
There are ethical issues surrounding the use of biofuels. For example, crops that could be used to feed people are used to provide the raw materials for biofuels instead. This could cause food shortages or increases in the price of food. There are other economic issues surrounding the use of biofuels, including:
- human resources -more people are needed to produce biofuels than are needed to produce petrol and diesel
- increased income - for farmers
- lower fuel prices - biofuels limit the demand for fossil fuels, helping to reduce increases in fuel prices.
There are environmental issues surrounding the use of biofuels. Biodiesel naturally contains little sulfur. For example, it may be said that they are carbon neutral – the amount of carbon dioxide released when they are used is the same as the amount absorbed by the plants as they grew. If so, this would reduce the production of this greenhouse gas. However, while biofuels produce less carbon dioxide overall, they are not carbon neutral. This is because fossil fuels are used in their production, for example in making fertilisers for the growing plants.